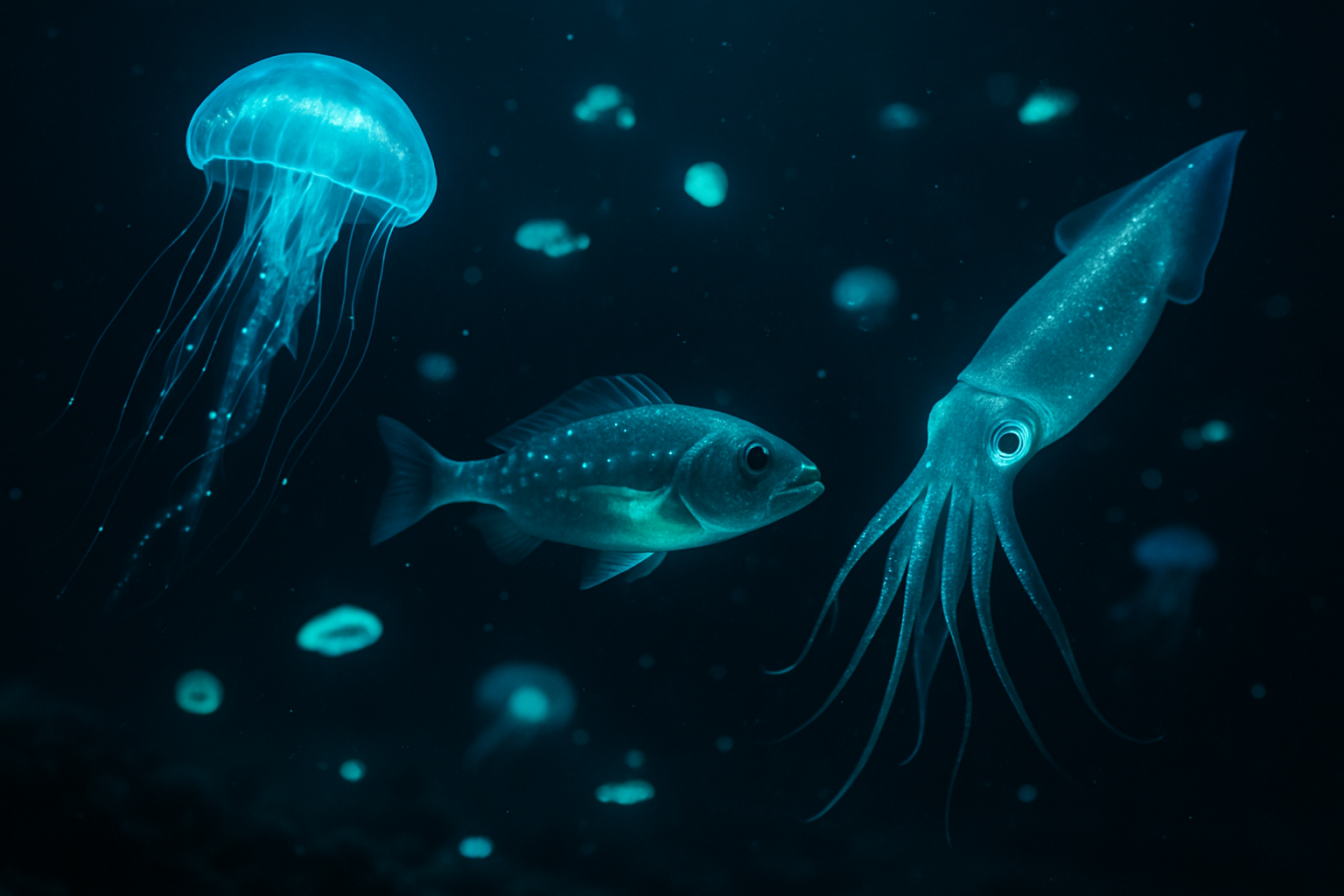
Unraveling the Enigma of Bioluminescent Marine Life
The mysterious glow of the ocean depths has captivated human imagination for centuries. Bioluminescent marine organisms, with their ability to produce light, create a mesmerizing spectacle that continues to intrigue scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. This fascinating phenomenon not only illuminates the dark corners of our oceans but also offers valuable insights into marine ecosystems and potential applications in various fields.

The Science Behind the Glow
At the heart of bioluminescence lies a complex chemical reaction. This process typically involves a light-emitting molecule called luciferin and an enzyme called luciferase. When these two components interact in the presence of oxygen, they produce light. The specific chemical makeup of these molecules can vary between species, resulting in different colors and intensities of light.
Interestingly, some marine organisms have evolved symbiotic relationships with bioluminescent bacteria. These microorganisms live within specialized light organs in the host, providing them with the ability to glow. This mutualistic relationship demonstrates the intricate interconnectedness of marine ecosystems and the diverse strategies organisms employ for survival.
Diverse Applications of Bioluminescence
The study of bioluminescent marine life has led to groundbreaking applications across various fields. In medical research, bioluminescent proteins have been used as markers to track cellular processes and gene expression. This has revolutionized our understanding of diseases and aided in the development of new treatments.
In environmental monitoring, bioluminescent organisms serve as sensitive indicators of water quality and pollution levels. Their presence or absence can provide valuable information about the health of marine ecosystems. Additionally, some researchers are exploring the potential use of bioluminescent algae as a sustainable source of lighting, potentially reducing our reliance on electricity in certain applications.
Bioluminescent Hotspots Around the World
While bioluminescence occurs throughout the world’s oceans, certain locations are renowned for their spectacular displays. The Mosquito Bay in Vieques, Puerto Rico, is often hailed as the brightest bioluminescent bay in the world. Here, microscopic dinoflagellates create a dazzling light show when disturbed, turning the water into a glowing blue canvas.
Another notable location is the Toyama Bay in Japan, where firefly squid congregate in large numbers during their spawning season. These small cephalopods emit a bright blue light, creating a mesmerizing spectacle that attracts tourists from around the globe. The estimated economic impact of bioluminescent tourism in these areas ranges from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars annually, highlighting the ecological and economic importance of preserving these unique marine habitats.
Conservation Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite their captivating beauty and scientific significance, bioluminescent marine organisms face numerous threats. Climate change, ocean acidification, and pollution pose significant risks to these delicate ecosystems. As water temperatures rise and pH levels decrease, many bioluminescent species struggle to adapt, potentially leading to population declines and ecosystem imbalances.
Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these remarkable creatures and the habitats they depend on. Researchers are working tirelessly to understand the specific environmental requirements of different bioluminescent species and develop strategies to mitigate the impacts of human activities on their populations.
Emerging Research and Discoveries
The field of marine bioluminescence continues to evolve, with new discoveries constantly expanding our understanding of this phenomenon. Recent studies have revealed previously unknown bioluminescent species in the deep sea, challenging our perceptions of biodiversity in these remote ecosystems.
Advancements in technology, such as deep-sea submersibles and high-sensitivity cameras, have enabled scientists to observe and document bioluminescence in its natural habitat with unprecedented detail. These observations provide valuable insights into the behavior, ecology, and evolution of bioluminescent organisms, paving the way for future research and conservation efforts.
As we continue to explore the depths of our oceans, the enigma of bioluminescent marine life remains a source of wonder and scientific inquiry. From its role in marine ecosystems to its potential applications in technology and medicine, bioluminescence serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and adaptability of life on our planet. By studying and preserving these glowing marvels, we not only unlock the secrets of the deep but also gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of life that sustains our oceans and, ultimately, our world.